Describe the Structure and Function of the Mitochondria
The chloroplast deals with the formation of sugars by utilizing the energy from the sun. Our library grows every minute-keep searching.

What Is The Structure And Function Of Mitochondria A Plus Topper
Double membrane bound organelles that are spherical to elongate in shape.

. For this reason the mitochondrion is sometimes referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria are the main site of ATP synthesis in aerobic cells using the free energy of the oxidation of metabolic fuels by oxygen. Mitochondria are derived from free-living alpha-proteobacteria that were engulfed by eukaryotic host cells through the process of endosymbiosis and therefore have their own DNA which is organized using basic proteins to form organelle nuclei nucleoids.
Mitochondrion are organelles within eukaryotic cells that produce adenosine triphosphate ATP the main energy molecule used by the cell. Outline why the cell needs energy The cell then uses energy to carry out the essential life processes aka MRS C GREN Describe the shape of a mitochondrion Rod-shaped. 8 Structure of ATP synthase consists of two protein entities.
Medium Solution Verified by Toppr The mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are associated with energy production or with the production of ATP. They are found in most mammalian cells with notable exceptions including mature erythrocytes. Mitochondria is regarded as the power house of the cell as it is the site of respiration.
The mitochondrial matrix is the site of organellar DNA replication transcription protein biosynthesis and numerous enzymatic reactions. The organelle is enclosed by two membranesa smooth outer membrane and a markedly folded or tubular. This is a sausage-shaped body surrounded by a double-membrane layer.
Mitochondrial DNA is compacted by the mitochondrial transcription factor TFAM into supramolecular assemblies called nucleoids of which there are about 1000 per cell 21. The mitochondria plays a major role in the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation which leads to the creation of ATP through the utilization of a hydrogen ion gradient the specifics can be seen in Campbells Biology text or any biochemistry book. 16 points answer 1 point grammarspelling 1 point citation 18 points Nucleus- the central and most important part of an object movement or group forming the basis for its activity and growth.
The mitochondria are organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are associated with energy production or with the production of ATP. Mitochondria is a structure used to provide energy for the various functions of the human body so it is a structure. Mitochondria are made up of two membranes- the outer and the inner membrane.
The general formula for glucose oxidation is. 1-Describe the structure and function of the following organelles. Browse 5 million homework and textbook solutions concept explainers videos and more.
Search concepts or drop in your homework problem. Mitochondria are made up of two membranes- the outer and the inner membrane. Hypothetically mitochondria are believed to have originated as prokaryotic cells like bacteria.
Functionconverts energy into a from the cell can use. The structural architecture and the organization into cellular compartments known as cell organelles enable eukaryotic cells to perform complex functions. It is thus often called the cells power- house.
It is a membrane-bound organelle present in the cytoplasm of the cell of Eukaryotic organisms which synthesizes energy molecules in the form of ATP which is used by the cell. Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration. - Is mitochondria a.
The energy producing reactions of cellular respiration take place in the mitochondria. The function of ATP synthase is to synthesise ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Mitochondria divide and are split amongst the daughter cells during cell proliferation.
Step-by-step solution Step 1 of 5 The eukaryotic cells have complex structures and functions. It has a diameter of 02-10μm and length 10-41μm. It ranges from 05 to 10 micrometer in diameter.
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell as they produce cellular energy in the form of ATP to keep the individual cells and the plant functioning. Each mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound structure. They are the central executioner of cells and control cellular homeostasis through involvement in nearly all aspects of metabolism.
Explain the structure and function of the mitochondria. The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell ATP and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur. Mitochondria are mobile plastic organelles that have a double-membrane structure.
It also contains looped mitochondrial DNA mitochondrial ribosomes and enzymes define mitochondria. Nucleus endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body mitochondria lysosomes ribosomes and centrioles. Mitochondria are found in all eukaryotes which are all living things that are not bacteria or.
Mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell which produces energy. The inner membrane form folds called the cristae that enclose the matrix. Mitochondria are double membrane-bound cell organelles with a typical size of 075-3 μm².
Homework help starts here. Classically referred to as the powerhouse of the cell they are the site of the majority of ATP synthesis and are therefore exceptionally important to function both microscopically. Science Biology QA Library Describe the structure and functions of mitochondria.
As our understanding of mitochondria has expanded it has become clear that the structure function and pathology of the. The inner membrane is folded to form partitions which project into the inside of the mitochondria. F1 is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and Fo is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Describe the primary function of mitochondria Site of cellular respiration- the production of energy in the form of ATP from glucose. Describe the matrix it is enclosed by thinner membrane and is semi-rigid and gel-like consisting of a mixture of proteins and lipids. Describe the structure and functions of mitochondria.
It has four distinct domains. The outer membrane the inner membrane the intermembrane space and the matrix. Was this answer helpful.
Describe the structure and functions of mitochondria. Mitochondria are now known to be more than the hub of energy metabolism. Mitochondria is about 1 mm in diameter and 1-10 mm in length.
They have a matrix space containing the enzymes of the citrate cycle and beta-oxidation enclosed by an inner membrane containing the 4 complexes of the electron transport chain ATP synthase and specific carriers for metabolites.

Function Of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Niche United States Function Smooth Eukaryotic Cell

Cell Structure And Function Exam 3 Mitochondria Flashcards Quizlet

Describe The Structure Of Mitochondria With The Help Of A Diagram Cbse Class 10 Science Learn Cbse Forum

Learn About Plant Cell Types And How They Re Like Animal Cells Prokaryotic Cell Cell Biology Plant Cell

5 Ways To Improve Your Health By Boosting Mitochondria Mitochondria Mitochondrial How To Increase Energy

Structure Of Mitochondria Biology Diagrams Cell Biology Mitochondria

Gas Exchange In Mammals Aim To Understand The Structure And Function Of The Lungs Objectives By The En Structure And Function Respiratory System Physiology

Mitochondria Structure And Function With Diagram Mitochondria Structure And Function Oxidative Phosphorylation
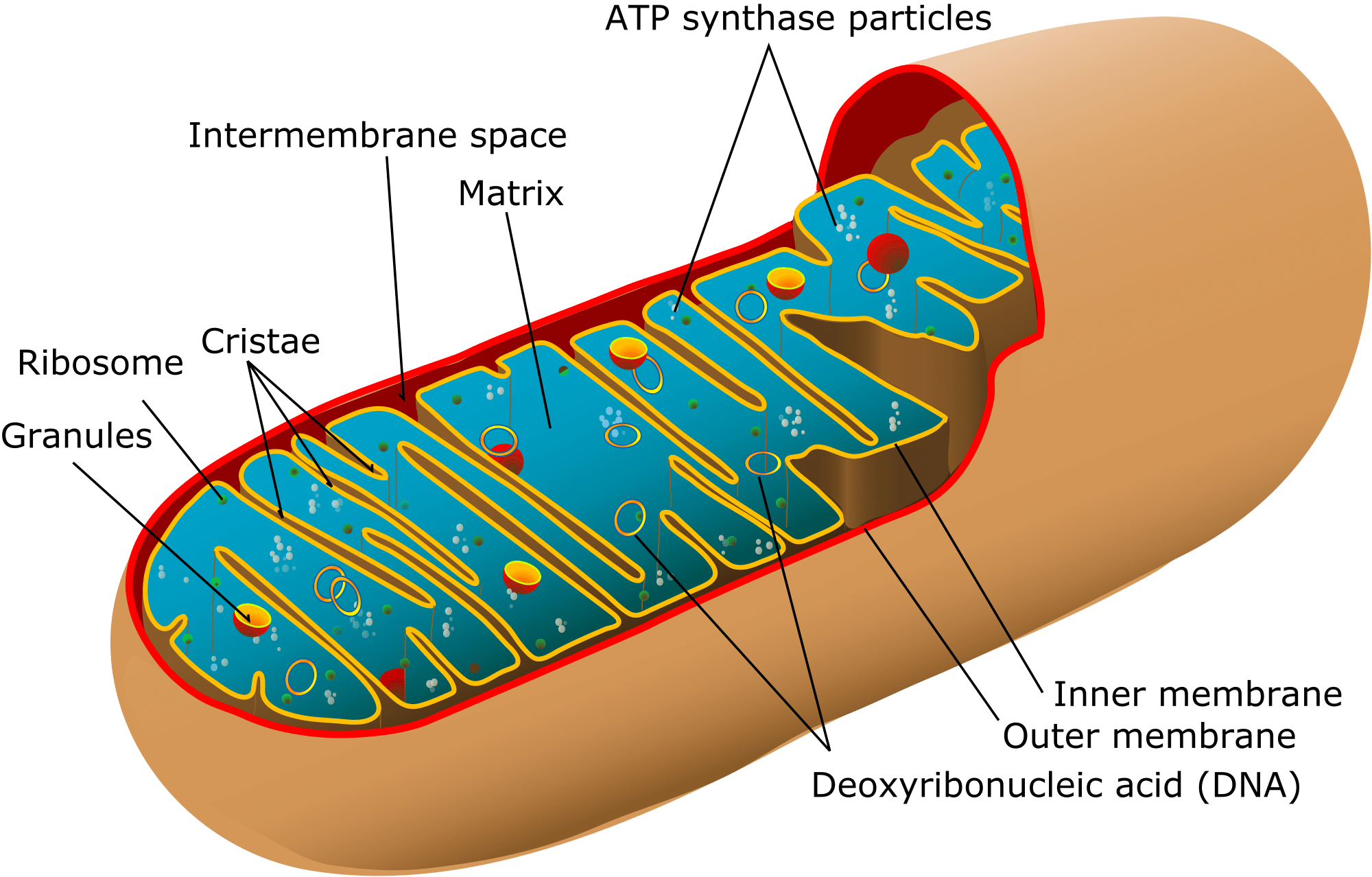
Mitochondria Structure Function Teachmephysiology

Mitochondria And Chloroplasts Worksheet Pdf Download Mitochondria Chemical Energy Worksheets

Difference Between Chloroplast And Mitochondria Structure Function Comparison Mitochondria Mitochondrial Cell Organelles
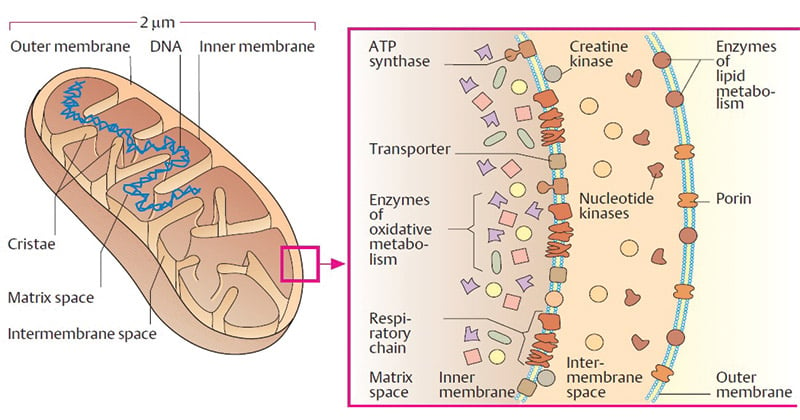
Mitochondria Definition Structure Functions And Diagram

Cell Organelles Structure And Functions With Labeled Diagram Cell Organelles Organelles Human Cell Structure

Mitochondria Structure Membrane Inner Matrix Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
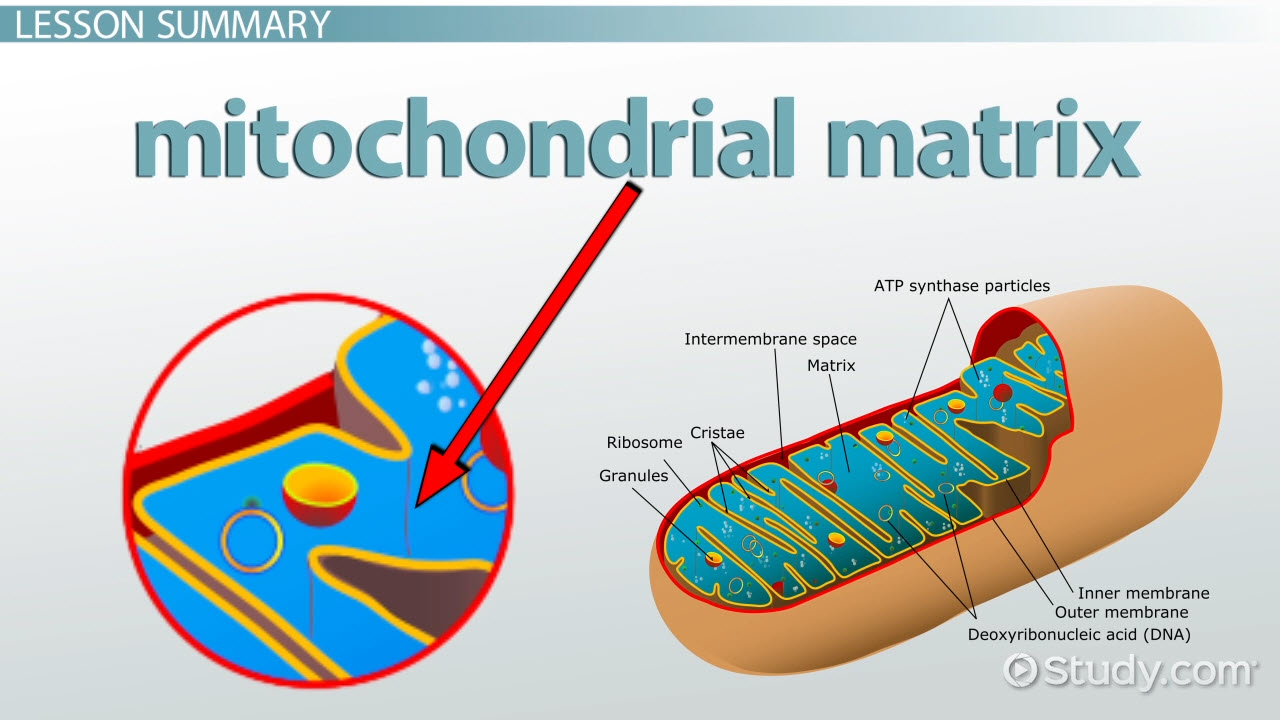
Parts Of A Mitochondria Diagram Ribosomes Function Of Mitochondrial Matrix Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Eukaryotic Cell Structure Eukaryotic Cell Cell Biology Cell Parts

The Structure Of Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough And Smooth Er Diagram Cell Membrane Structure And Function Things Under A Microscope


Comments
Post a Comment